Many individuals worldwide need reliable internet to work, communicate, and manage daily tasks. Staying online at all times can be expensive, especially when traveling or living in areas with limited connectivity.
This comprehensive guide explains how you can find and use free Wi-Fi on mobile devices through various strategies, apps, and security measures. Every section focuses on practical tips to ensure a secure and stable connection.
Importance of Free Wi-Fi for Mobile Users
A strong Wi-Fi connection is a cornerstone of modern life, enabling people to perform crucial activities quickly and efficiently. Reliable access to the internet drives global communication, supports remote work, and entertains everyone.
This is why free Wi-Fi is becoming more accessible in different parts of the world, as businesses, communities, and local programs recognize the importance of connectivity.
Free Wi-Fi hotspots address these issues by offering immediate internet access that does not involve extra data fees or complicated agreements. Frequent travelers benefit substantially from such networks, as free Wi-Fi saves money on roaming fees and prevents interruptions.
Primary Methods of Finding Free Wi-Fi
Technology continues to evolve in ways that help you stay connected. Various tools and techniques can assist in locating free networks wherever you happen to be.
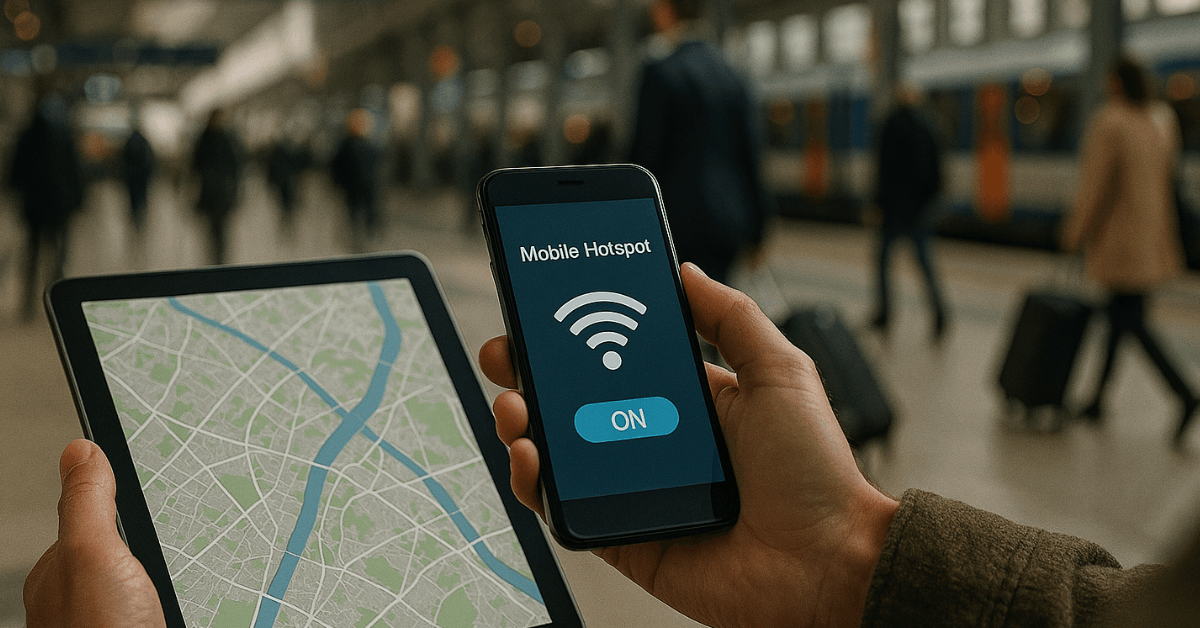

Thorough knowledge of these options will help you maintain a stable internet connection on the go, whether you need to check an important email or browse casually.
1. Public Hotspots in Common Places
Many businesses and public areas worldwide offer accessible Wi-Fi connections to their patrons.
Cafes, shopping malls, libraries, restaurants, and certain transit stations regularly host open hotspots. These locations use free Wi-Fi to attract more visitors or improve customer satisfaction.
Keeping track of places like libraries can be especially beneficial, since they often provide stable and reliable connections. Choosing public hotspots in popular areas can simplify your search for free Wi-Fi.
Certain public plazas or major attractions host city-wide programs that create multiple hotspots for residents and visitors. Governments sometimes collaborate with private companies to provide broader coverage in busy spots, enhancing internet availability for everyone.
2. Apps Designed to Locate Free Wi-Fi
Hotspot-finder applications leverage community feedback and user-generated data. These apps show which hotspots are nearby and whether they are secure, password-protected, or entirely free.
They can also indicate network speeds, reliability, and user reviews. Features like offline maps make planning simpler if you expect limited coverage.
Several options dominate this category, each offering distinct advantages:
- WiFi Map: Curates a large database of hotspot details, including shared passwords.
- Instabridge: Provides crowd-sourced public hotspots and a straightforward interface for quick connections.
- WiFi Finder: Focuses on verified public hotspots and allows filtering by venue type.
- WiFi Master: Helps users connect automatically to available networks, minimizing manual steps.
- Boingo Wi-Finder: Features an extensive network of hotspots in partnership with various businesses.
These apps typically rely on user participation to maintain up-to-date working hotspot lists. User ratings and speed tests can guide you toward networks that suit your requirements.
3. Sharing Internet Through Mobile Hotspots
Modern smartphones can serve as portable hotspots. This functionality lets you share mobile data with additional devices, including laptops and tablets. Enabling a hotspot on a phone is straightforward on both Android and iOS.
Securing the shared connection with a strong password ensures that only trusted parties can join.
This approach proves invaluable in areas lacking reliable Wi-Fi. Adopting your phone as a hotspot can provide immediate internet for essential tasks. However, it may consume mobile data quickly, so keep track of data limitations to avoid extra charges.
4. Traveling with a Portable Router
Carrying a portable router transforms cellular signals into Wi-Fi for multiple devices at once. This solution is popular worldwide among travelers who require a dedicated network while on the move. Portable routers function like standard routers but rely on SIM cards to connect to cellular networks.
Speeds vary based on local network coverage, and battery life differs among models. Although you must purchase data for a portable router, having full control over your network is a significant advantage.
Personal routers often provide stronger security measures than public hotspots, giving you more confidence about data protection. Devices like laptops, tablets, and phones all connect seamlessly through this centralized point.
5. Accessing Less-Visible Networks
Hidden Wi-Fi networks do not openly broadcast their SSIDs. These networks are typically overlooked by users who rely on standard scanning methods. You can locate them using specialized Wi-Fi analyzer tools that detect nearby signals.
Although connecting to hidden networks requires manually entering the SSID and security details, taking these extra steps might pay off if other connections are weak or unavailable.
Hidden networks remain less crowded because they are not easily visible, which sometimes means more stable speeds. Be sure you have the correct password and security information to avoid misconfiguration or unintended issues.
Keeping Connections Secure on Public Wi-Fi
Utilizing a free network might expose your data to potential risks if security measures are weak. Hackers can intercept sensitive information in unprotected environments. Basic security awareness is essential when connecting to any public network.
Choose Trusted Networks
Stick to recognized hotspots from legitimate businesses or government initiatives. Malicious networks sometimes disguise themselves to trick unsuspecting users.
Verifying network names before connecting can help you avoid risky connections cybercriminals create.
Use a VPN
Implementing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) is an effective way to add encryption. VPN apps create secure tunnels for your data, so third parties cannot monitor browsing habits.
Sensitive activities, such as logging into email or accessing banking services, become safer through an encrypted VPN. Many VPN services are available with a variety of performance levels.
Free options can be enough for light usage, while premium services offer advanced security settings and faster speeds. An encrypted tunnel means hackers monitoring the network see only scrambled data, keeping your personal details hidden.
Refrain from Sensitive Transactions
Public hotspots frequently lack strong security protocols, making them less reliable for confidential operations.
Financial or personal data transactions should wait until you can use a secure, password-protected connection. Bank transactions, online shopping, and other tasks requiring sensitive information are safer when performed on a trusted network.
Keep Devices Updated
Regularly updating operating systems, security patches, and antivirus software guards against vulnerabilities that hackers exploit.
Updates often fix loopholes discovered in previous versions, so skipping them can expose your device. A device with outdated security lacks critical defenses and may be an easy target for threats.
Disable Auto-Connect
Certain devices automatically join recognized networks after the first connection.
Turning this off prevents surprise connections to questionable networks that share similar names. Going through manual steps to join each network ensures that you are aware of exactly where you are connecting.
Government and Private Initiatives
Some regions run projects that aim to deliver widespread free internet access. Public agencies partner with private entities to sponsor open hotspots in congested areas, community centers, or educational facilities.
These initiatives help bridge the digital divide by providing essential services for individuals worldwide. Look for local government websites or community boards listing available Wi-Fi zones.
In many places, official support pages offer maps or directories of connectivity programs. Enrollment for certain programs might require filling out an application, but many hotspots remain open to everyone without extra steps.
Practical Tips for a Stable Connection
Strong signals, minimal interference, and minimal competition from other users lead to better experiences. Understanding how to enhance stability can make free hotspots more efficient.
- Stay Near the Source: Closer proximity to the router or hotspot source can enhance signal strength. Connecting in an uncrowded area, when possible, could result in improved speeds and reduced dropouts.
- Pick Networks with Higher Ratings: Applications that show community ratings can help you decide which networks to use. Feedback from other users helps identify hotspots known for reliable speeds and fewer interruptions.
- Limit Background Data Usage: Closing unnecessary apps and tabs that run extensive background tasks can maintain decent performance while connected to free networks. Streaming high-resolution content, large downloads, or multiple uploads can quickly choke limited bandwidth.
- Try Different Times: Peak hours, especially in popular establishments, might lead to heavy congestion and slower connections. Off-peak times often offer smoother performance, making it easier to accomplish critical online tasks.
Overcoming Common Connection Issues
Free Wi-Fi can occasionally be slow or unstable. Diagnosing common problems can help you avoid missing essential emails or calls at inconvenient moments.
- Connection Drops Suddenly: Switching between networks or relocating to an area with stronger coverage can help.
- Low Speed: Checking if the hotspot is congested or if signal strength is weak may explain poor performance.
- Login Portals Not Appearing: Certain public networks use a login portal before granting full access. Manually opening a browser and visiting a non-encrypted site can trigger the login screen.
- App Crashes: Clearing app cache or restarting the app often resolves minor software glitches that prevent proper network scanning.
Leveraging Offline Maps and Guidance
Even with free Wi-Fi readily available, offline maps help you navigate in areas with spotty connections. Several apps offer the ability to download city or regional maps.
Planning ahead ensures that you can locate Wi-Fi hotspots, travel routes, or tourist attractions without worrying about coverage gaps. Offline functionality pairs well with hotspot-finder apps, since certain platforms allow you to save hotspot databases for later reference.
This is especially useful if you anticipate traveling to regions where networks are less common or the signal is intermittent.
Responsible Usage and Etiquette
Since businesses or communities sponsor many free hotspots, responsible usage encourages these networks to remain accessible. Taking simple steps to respect bandwidth and ensure security is a courtesy to everyone sharing the resource.
- Avoid Large Downloads: Activities like massive file downloads strain limited bandwidth and reduce speeds for everyone else.
- Log Out After Use: Signing out of connected services and disabling auto-connect helps maintain security.
- Limit Multimedia Streaming: Video or music streaming on a free hotspot can degrade speeds for other users relying on the same connection.
Conclusion
A strong internet connection is essential for work, entertainment, and communication. Free Wi-Fi is beneficial in areas with high data costs or poor coverage. You can stay connected almost anywhere by using the right tools and practicing safe habits.
Trusted networks and hotspot-finder apps make it easier to browse securely and avoid disruptions.